
The UAE banking sector has demonstrated remarkable resilience and growth in 2023 and 2024, despite global economic uncertainties and the introduction of a federal corporate tax regime in 2023. This post explores the performance of three leading UAE banks—Mashreq, First Abu Dhabi Bank (FAB), and Emirates NBD—highlighting their financial results, key drivers of growth, and the broader implications for the UAE economy. Additionally, we compare the UAE banking sector’s performance with global trends, underscoring its competitive edge.
The UAE banking sector has been a cornerstone of the nation’s economic diversification strategy. In 2023 and 2024, the sector continued to thrive, driven by robust economic activity, higher interest rates, and increased demand for credit. The implementation of a 9% federal corporate tax in 2023, while a significant policy shift, had minimal impact on the profitability of banks due to their strong fundamentals and adaptability.
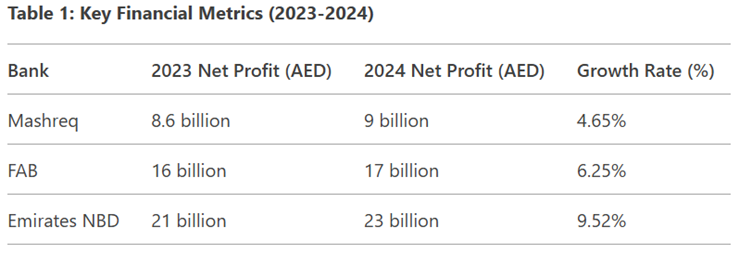
Here are some key statistics for the years ending on 2024 and 2023:
- Total Assets of UAE Banking Sector: AED 4.1 trillion (2024), up from AED 3.9 trillion (2023).
- Total Loans and Advances: AED 1.9 trillion (2024), a 6% increase from 2023.
- Net Profits of Top 3 Banks: AED 49 billion (2024), up from AED 45.6 billion (2023).
- General performance of leading UAE banks
The banking sector in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has shown resilience and adaptability in the face of global economic fluctuations, leveraging digital transformation, robust regulatory frameworks, and diversified revenue streams. This analysis critically examines the financial performance of Mashreq Bank, First Abu Dhabi Bank (FAB), and Emirates NBD based on their net profit figures from 2023 and 2024, highlighting key growth drivers, challenges, and strategic approaches that have influenced their earnings.
Key Growth Drivers
Growth in the banking sector is driven by multiple key factors that contribute to the expansion of financial institutions and their ability to navigate economic fluctuations. One of the most significant drivers of growth is digital transformation, which has revolutionized the banking experience for both customers and financial institutions. Banks have heavily invested in digital banking solutions, enabling seamless transactions, mobile banking, and AI-driven customer service. This technological shift has not only improved customer engagement but has also significantly reduced operational costs by automating processes that were traditionally labor-intensive. A prime example is the rise of digital-only banks and fintech companies, which have successfully challenged traditional banking models by offering innovative financial solutions.
Another crucial factor in banking growth is the higher interest rate environment, which directly impacts net interest income—the primary revenue source for most banks. When interest rates rise, banks earn higher margins on loans and credit facilities, leading to increased profitability. This is particularly beneficial for institutions with diversified lending portfolios, as they can capitalize on rate hikes while maintaining a balance between loan disbursements and deposit rates. However, banks must carefully manage credit risk in such environments to prevent an increase in non-performing loans (NPLs), which could offset the gains from higher interest income.
The expansion of loan portfolios is another major growth driver, as it allows banks to increase their revenue streams through higher lending activity. Institutions that actively grow their loan books while maintaining a healthy loan-to-deposit ratio are better positioned to sustain long-term profitability. Lending to high-growth sectors such as real estate, infrastructure, and technology provides lucrative opportunities, as these industries often require significant financing. Banks that successfully expand their lending operations while maintaining strict credit evaluation processes are more likely to experience stable growth and reduced default risks.
Cost efficiency measures also play a pivotal role in enhancing profitability and operational sustainability. Many banks have undertaken aggressive restructuring efforts, including branch rationalization, automation of back-office functions, and staff optimization, to reduce unnecessary expenditures. The adoption of AI-powered financial analysis and chatbot-assisted customer service has significantly reduced the reliance on manual processes, improving efficiency and cutting costs. Banks that effectively manage their cost structures can reinvest savings into strategic growth areas such as digital banking and customer acquisition.
Another fundamental aspect of banking growth is the development of diversified revenue streams. Banks that rely solely on traditional lending and deposit-taking activities are more vulnerable to economic downturns and interest rate fluctuations. To mitigate this risk, institutions have expanded into corporate banking, wealth management, and investment advisory services. Additionally, many banks have capitalized on the surge in demand for sustainable finance and Islamic banking, offering specialized financial products that cater to niche markets. This diversification allows banks to generate stable revenue even in volatile economic conditions.
Strategic international expansion has become a common approach for banks seeking to increase their market presence and access new customer bases. By establishing operations in high-growth regions such as Asia, Europe, and the Middle East, banks can tap into emerging markets with strong economic potential. This expansion not only enhances revenue diversification but also strengthens the bank’s resilience against localized economic downturns. The success of international expansion, however, depends on an institution’s ability to navigate different regulatory environments and adapt to varying customer preferences.
The role of technological advancements cannot be understated in driving banking growth. Artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and big data analytics have transformed the financial landscape by enhancing fraud detection, improving risk assessment, and personalizing customer experiences. Banks that integrate AI-driven banking solutions can offer faster loan approvals, predictive analytics for customer spending behavior, and real-time fraud monitoring, thereby strengthening customer trust and operational efficiency.
Robust asset quality is another key factor that determines a bank’s ability to grow sustainably. Institutions that maintain strong risk management frameworks and prudent lending policies are better equipped to handle economic downturns and financial crises. By keeping non-performing loans (NPLs) at a minimum, banks can preserve their financial health and avoid significant losses. This requires continuous monitoring of loan performance, proactive restructuring of distressed assets, and adherence to stringent credit evaluation standards.
The presence of a strong retail and corporate banking network is fundamental for banks aiming to dominate in competitive financial markets. Retail banking provides steady income from consumer loans, mortgages, and credit cards, while corporate banking generates substantial revenue from business loans, trade finance, and treasury services. Banks that successfully balance both segments can create a diversified income stream that minimizes reliance on any single revenue source. In highly competitive banking sectors, institutions that offer seamless digital experiences, competitive interest rates, and tailored financial solutions tend to attract and retain a larger customer base.
Digital innovation and AI integration have played an increasingly important role in redefining the customer banking experience. Banks have embraced AI-powered chatbots, automated investment advisory services, and digital wallets to meet the evolving demands of tech-savvy consumers. These innovations not only enhance customer convenience but also streamline internal processes, improving overall efficiency. Financial institutions that continue to invest in technological advancements position themselves at the forefront of industry evolution.
The development of a diversified lending portfolio is crucial in mitigating risk and sustaining long-term growth. Banks that lend across multiple industries, including real estate, manufacturing, healthcare, and technology, reduce their exposure to sector-specific downturns. A well-balanced loan book ensures financial stability, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty, by distributing risk across different markets.
Finally, expanding presence in the GCC and international markets has been a significant driver of growth for banks seeking to diversify their revenue streams beyond domestic markets. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region, with its thriving financial sector and ambitious economic diversification plans, presents ample opportunities for banks to expand their footprint. Establishing operations in countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and other MENA markets allows financial institutions to tap into new client bases, increase cross-border trade finance, and leverage the region’s economic growth initiatives.
